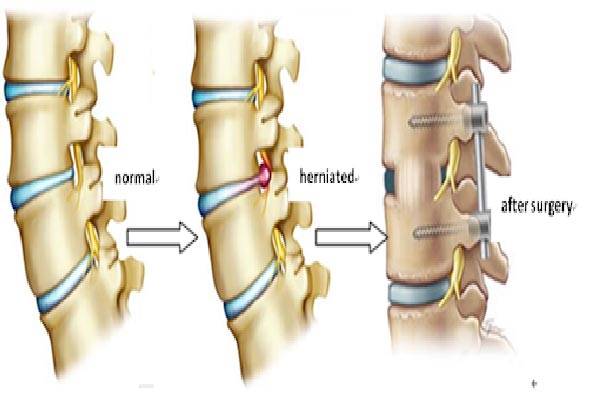
Spinal disc:
herniation is an injury to the cushioning and connective tissue between vertebrae, usually caused by excessive strain or trauma to the spine. It may result in back pain, pain or sensation in different parts of the body, and physical disability. The most conclusive diagnostic tool for disc herniation is MRI, and treatment may range from painkillers to surgery. Protection from disc herniation is best provided by core strength and an awareness of body mechanics including posture.
When a tear in the outer, fibrous ring of an intervertebral disc allows the soft, central portion to bulge out beyond the damaged outer rings, the disc is said to be herniated.
Disc herniation is frequently associated with age-related degeneration of the outer ring, known as the annulus fibrosus, but is normally triggered by trauma or straining by lifting or twisting. Tears are almost always postero-lateral (on the back of the sides) owing to the presence of the posterior longitudinal ligament in the spinal canal. A tear in the disc ring may result in the release of chemicals causing inflammation, which can result in severe pain even in the absence of nerve root compression.
Disc herniation is normally a further development of a previously existing disc protrusion, in which the outermost layers of the annulus fibrosus are still intact, but can bulge when the disc is under pressure. In contrast to a herniation, none of the central portion escapes beyond the outer layers. Most minor herniations heal within several weeks. Anti-inflammatory treatments for pain associated with disc herniation, protrusion, bulge, or disc tear are generally effective. Severe herniations may not heal of their own accord and may require surgery.
Cause:
When the spine is straight, such as in standing or lying down, internal pressure is equalized on all parts of the discs. While sitting or bending to lift, internal pressure on a disc can move from 17 psi (lying down) to over 300 psi (lifting with a rounded back). Herniation of the contents of the disc into the spinal canal often occurs when the anterior side (stomach side) of the disc is compressed while sitting or bending forward, and the contents (nucleus pulposus) get pressed against the tightly stretched and thinned membrane (annulus fibrosus) on the posterior side (back side) of the disc. The combination of membrane-thinning from stretching and increased internal pressure (200 to 300 psi) results in the rupture of the confining membrane. The jelly-like contents of the disc then move into the spinal canal, pressing against the spinal nerves, which may produce intense and potentially disabling pain and other symptoms.
Some authors favour degeneration of the intervertebral disc as the major cause of spinal disc herniation and cite trauma as a minor cause. Disc degeneration occurs both in degenerative disc disease and aging. With degeneration, the disc components – the nucleus pulposus and annulus fibrosus – become exposed to altered loads. Specifically, the nucleus becomes fibrous and stiff and less able to bear load. Excess load is transferred to the annulus, which may then develop fissures as a result. If the fissures reach the periphery of the annulus, the nuclear material can pass through as a disc herniation.
Several genes have been implicated in intervertebral disc degeneration. Probable candidate genes include type I collagen (sp1 site), type IX collagen, vitamin D receptor, aggrecan, asporin, MMP3, interleukin-1, and interleukin-6 polymorphisms. Mutation in genes – such as MMP2 and THBS2 – that encode for proteins involved in the regulation of the extracellular matrix has been shown to contribute to lumbar disc herniation.
Disc herniations can result from general wear and tear, such as constant sitting or squatting, driving, or a sedentary lifestyle.Herniations can also result from the lifting of heavy loads.
Professional athletes, especially those playing contact sports such as American football, are known to be prone to disc herniations. Within athletic contexts, herniation is often the result of sudden blunt impacts against, or abrupt bending or torsional movements of, the lower back.

دوره تخصص خود را در دانشگاه های علوم پزشکی شهید بهشتی و علوم پزشکی گیلان ( بخش پروفسور مجید سمیعی ) گذرانده اند ، ایشان عضو انجمن جراحان مغز و اعصاب ایران می باشند .